Travel and vaccination are two things that often come together. It is of great importance to be familiar with vaccination requirements when traveling to certain countries, because in many cases, proper and timely vaccination saves life.
In this text, I explain in which case and against which diseases travel and vaccination go together. I added a table with all countires and teritorries with their requirements for vaccination and health safety.
For complete understanding, I recommend reading the entire text.
You will thank me later.
Follow me on Instagram and Facebook!
YELLOW FEVER – TRAVEL AND MANDATORY VACCINATION
Vaccination is mandatory in countries where the yellow fever virus is transmitted by mosquitoes. This is a serious type of infection that the population in the marked countries is fighting against every day. It is necessary to get vaccinated before traveling and show a certificate of vaccination when entering the country.
The virus is transmitted when a mosquito previously bites an already infected person, and the mosquito transmits it as a vector to a healthy individual.
YELLOW FEVER – TRAVEL AND VACCINATION IS CONDITIONALLY MANDATORY
Proof of vaccination must be submitted to the country into which travelers are entering, in case they have arrived from a country that belongs to the group of risk countries with widespread Yellow Fever, and affected by the risk of infection.
YELLOW FEVER – TRAVEL AND VACCINATION IS NOT MANDATORY
Countries marked in green do not pose a risk of infection and disease transmission. The type of mosquitoes that transmit the virus are not present in those regions.
MALARIA – MANDATORY TAKING ANITMALARIKA TABLETS
Malaria is an infectious disease that is also transmitted by mosquitoes. This time it is not a virus, but Plasmodium. Plasmodium is a eukaryotic microorganism that, when it enters the body, acts by destroying erythrocytes or red blood cells. This leads to serious and long-term health problems that can result in a high degree of anemia, which prevents the erythrocytes from carrying oxygen to all cells in the body.
The indicated countries carry the risk of the possibility of malaria transmission during the stay. On the other hand, in some countries only some parts of the country are at risk.
It is best to consult a doctor early before the trip, because in some cases, taking antimalarial drugs can start several months before the trip itself.
It is important to remember that the pills are only preventive and do not protect completely. You should definitely avoid mosquito bites by wearing long clothes, using mosquito sprays and sleeping in nets at night.
MALARIA – TAKING ANTI-MALARIA TABLETS IS NOT MANDATORY(marked in green).
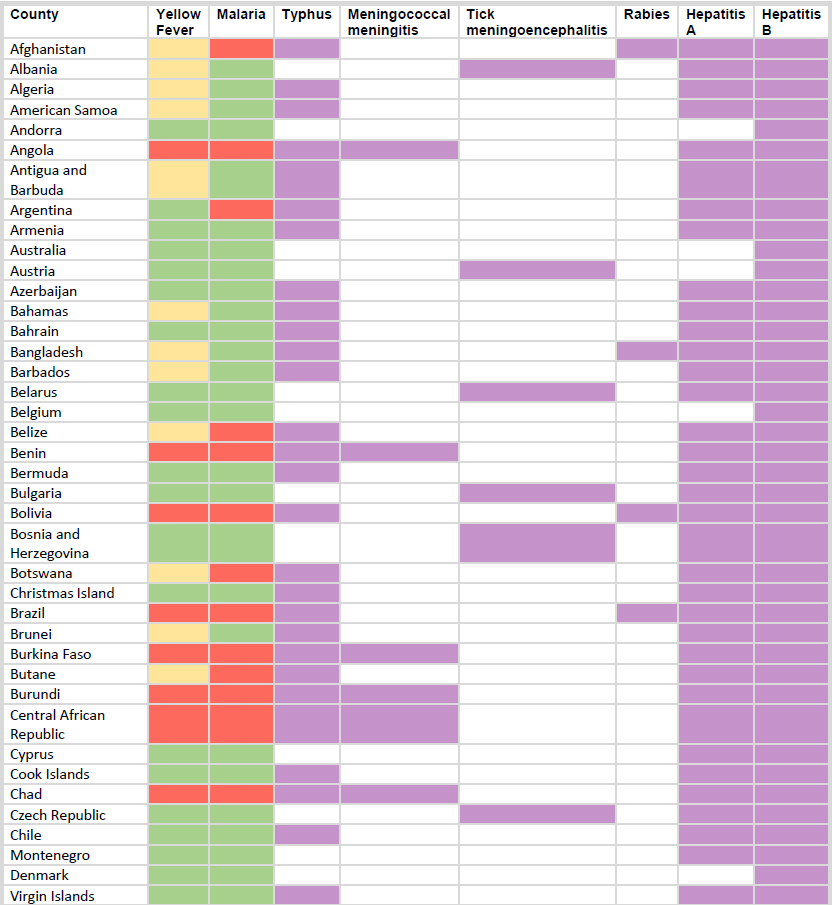
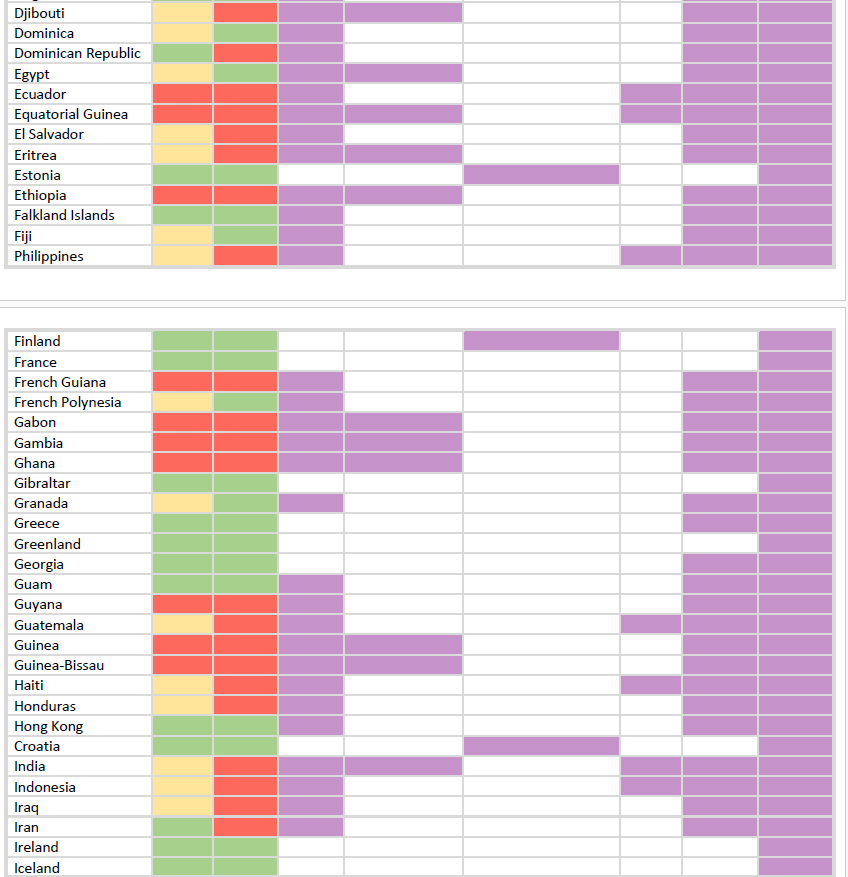
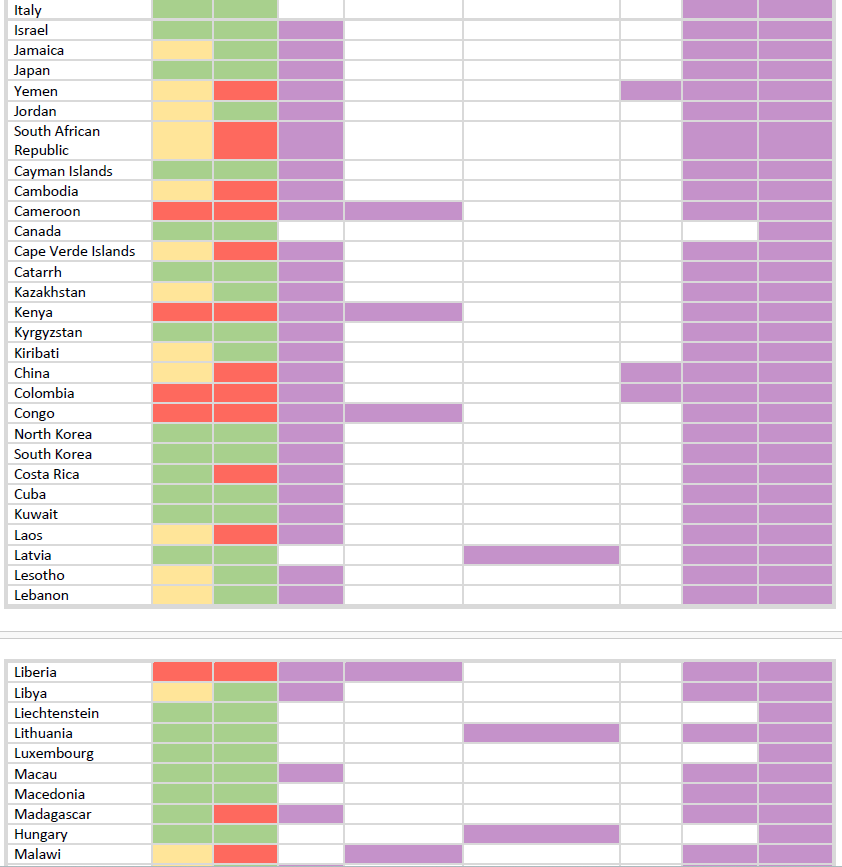
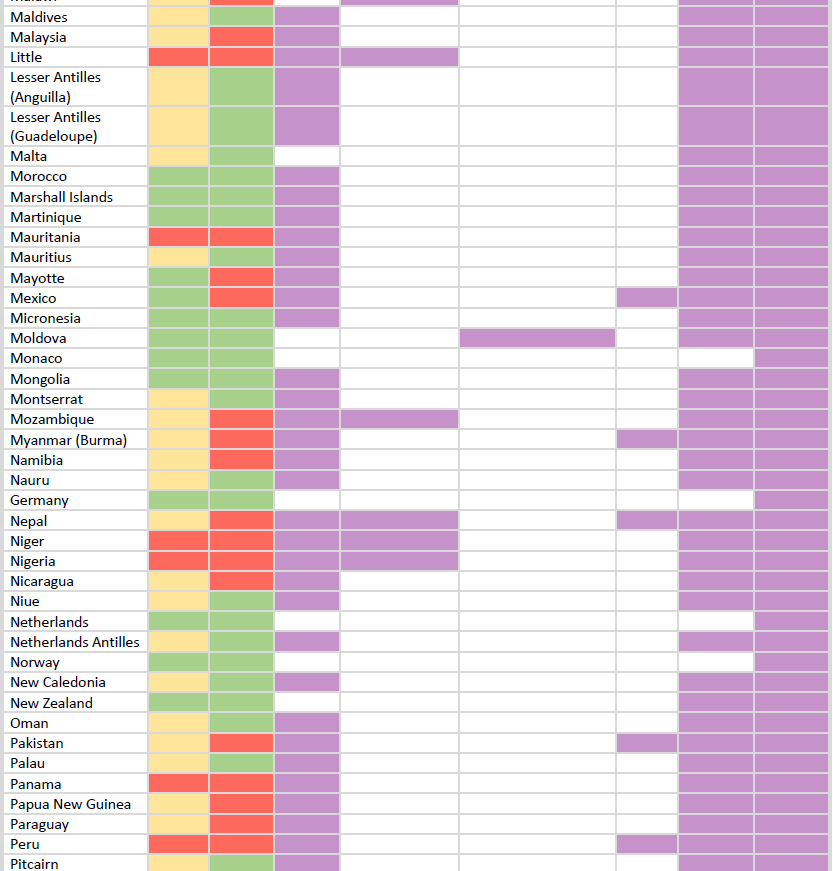
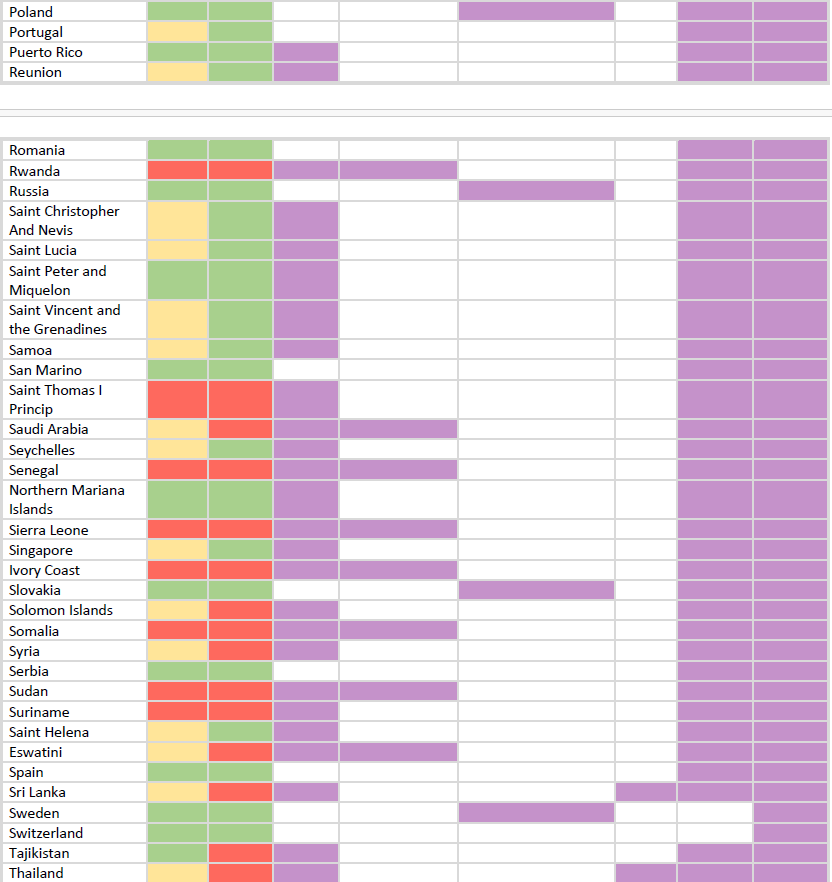
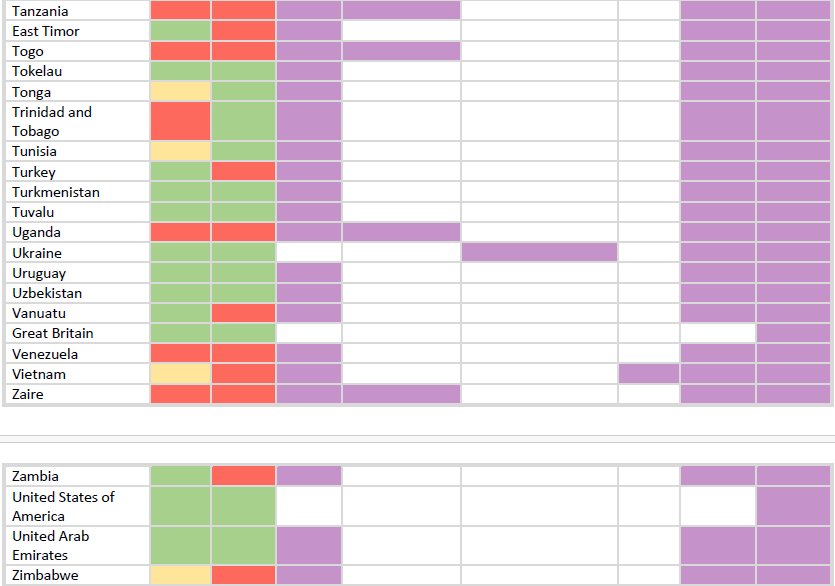
Download the table HERE.
TRAVEL AND VACCINATION IS RECOMMENDED:
For the mentioned diseases and countries marked in purple, it is best to consult a doctor or an epidemiologist.
Vaccination tables in regions are created depending on the need and the general occurrence of the disease in an area. This mostly depends on the carrier or vector, which can be mosquitoes, ticks or animals, and in some cases also the tendency to pollute water and food, or bacteria.
In addition to the location, the situation largely depends on the time of year, planned activities, parts of the country you plan to visit, etc.
TYPHUS/ Typhoid
Typhoid, or “stomach typhus”, is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi.
It is spread through food and water due to inadequate hygiene and poor sanitary conditions. It comes from feces and urine. Flies are also frequent carriers of this unpleasant infection. In case of inadequate treatment, the patient becomes a chronic germ carrier. The bacterium is present permanently and mostly does not bother the host, but is capable of infecting others.
RABIES
Rabies is transmitted by the bite of a “rabid” animal. This disease consists of a virus as the main protagonist that attacks the central nervous system. It is found in the saliva of an infected animal. It can be transmitted by various domestic and wild animals. Including dogs, foxes, wolves, raccoons, BATS, rats, mice and cats.
The great advantage of this virus is that the farther the bite is from the central nervous system and the brain, the better the prognosis for recovery. The reason for this is that the virus travels slowly, and its final destination is the brain. So the incubation period can be from a week to several months if the bite is far from the brain, such as on the foot or arm.
In any case, rabies can happen in absolutely any part of the world and this should not be joked about because the consequences can be terrifying. It is necessary to get an injection against rabies as soon as possible.
The injection is most often given in the area of the bite.
TICK MENINGOENCEPHALITIS
It is most prevalent in certain parts of Europe and North America. It is caused by a virus transmitted by ticks. This disease affects different parts of the brain.
It is important to protect yourself from potential tick bites in general. This is best done with adequate clothes and shoes.
You should also pay attention to the type of clothing. Wide clothes can’t stop them from crawling in.
MENINGOCOCCAL MENINGITIS OR MENINGOCOCCAL SEPSIS
Inflammation of the meninges caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis. The infection is somewhat more common in children. It causes unpleasant symptoms on the whole body, inside and out. From bleeding, measles to fever.
The source of infection is another person infested with vacterium. Often a patient without symptoms. The bacterium can settle in the upper respiratory tract and wait there for some time until another viral infection or a decline in immunity occurs in order to attack its host.
HEPATITIS A i B
There are 7 types of hepatitis (for now) – A, B, C, D, E, F, G. Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver caused by a virus, and the severity and outcome of the situation mostly depends on which of these 7 types of hepatitis is present. Hepatitis is transmitted from person to person. through saliva, blood and other body fluids, also can be transmitted from contaminated food and water or thru needles and blood.
Vaccination against Hepatitis B is mandatory in developed countries. Kids get vaccinated in middle school.
Vaccination against Hepatitis A is not mandatory, at least not in European countries, but it is recommended.
What exactly is a vaccine?
Vaccination creates artificial immunity. In other words, the vaccine contains some form of a specific pathogen. It can be a “numbed/weak” virus, bacteria, or antigen to which our immune system will react and create antibodies. Now, in case of a real infection, our body is ready to fight, it has already made a DIY weapon and the pathogen has absolutely no chance!
Take a look at my eternal travel inspiration Pinterest and see you on Instagram.


Odgovori